Transfer Case Noise
There are different types of transfer cases. Many part-time 4WD vehicles contain transfer cases that have electric motors and solenoids to control case operation.
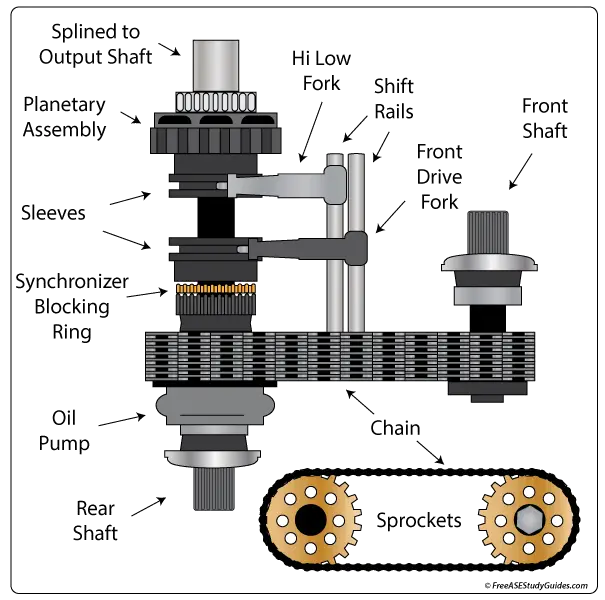
The module controls a motor that moves a set of rails and forks. The range or Hi-Low fork controls the planetary carrier. Moving the sleeve from the sun gear (1:1) to the planetary carrier increases torque over speed with a gear reduction of around (2.75:1). This low gear ratio varies between manufacturers.
The mode or front-drive fork moves a synchronizer sleeve that locks the drive sprocket to the output shaft, transferring power to the driven sprocket through a thick chain; this engages 4WD. Many vehicles use an open center differential transfer case that contains an additional planetary gearset to compensate for axle speed differential.
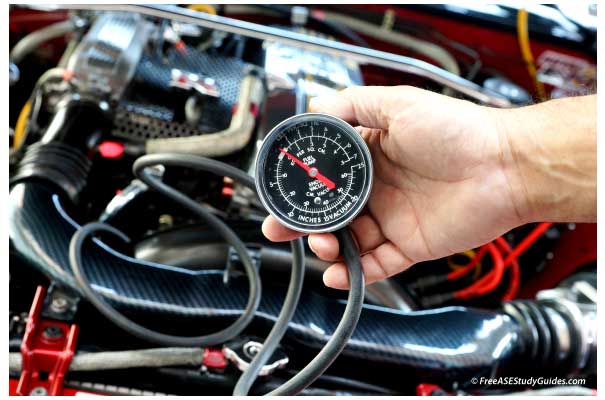

Some transfer cases are controlled by vacuum. Make sure the case receives the specified engine vacuum to ensure proper shifting. The vacuum is usually around 18-21 "hg. It's vital to understand the type of transfer case before beginning diagnostics.