Exhaust Color Diagnosis
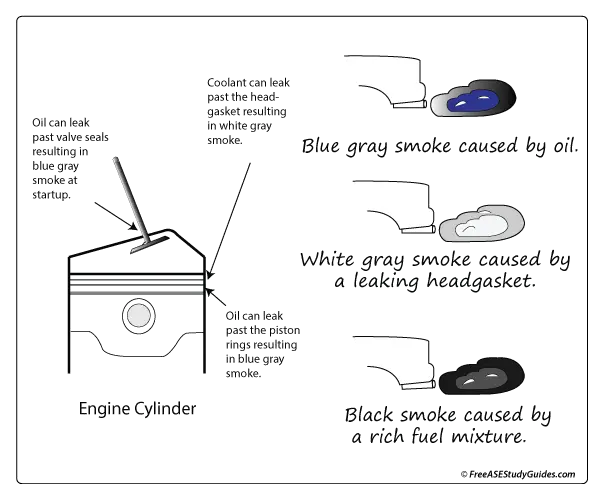
A rich or lean fuel condition and fluids leaking into a cylinder can damage the catalytic converter and result in colored exhaust. Exhaust color can indicate a problem with the engine's combustion.
Blue/gray Exhaust
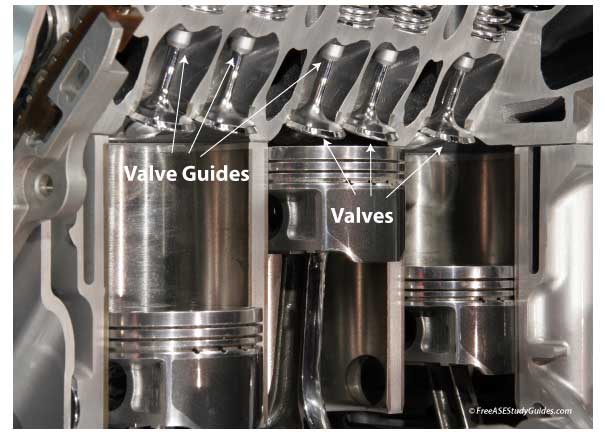

Blue/gray exhaust is an indication of oil burning in the combustion chamber. These are possible symptoms and causes:
Valve Seals: Leaking valve seals will cause blue/gray exhaust smoke.
Valve Guides: Excessive clearance between the valve stem and the valve guide allows the oil to leak past the gap into the cylinder.
Piston Rings: Worn or damaged piston rings will cause blow-by, resulting in blue/gray smoke.
Worn Cylinder Walls: Worn cylinder walls also cause blow-by, resulting in blue/gray smoke.
PCV System: A stuck closed PCV valve causes excessive crankcase pressure, resulting in blue/gray exhaust.
Black Exhaust
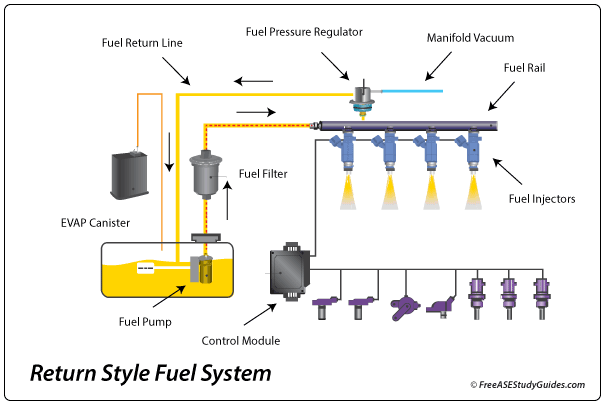
Black exhaust smoke is an indication of a rich fuel condition. These are possible causes:
Fuel Injectors: A leaking or dripping fuel injector will cause a rich fuel condition.
Fuel Pressure Regulator: A stuck closed fuel pressure regulator will cause a rich fuel condition.
Fuel Return: A restricted fuel return line will cause a rich fuel condition.
White Exhaust
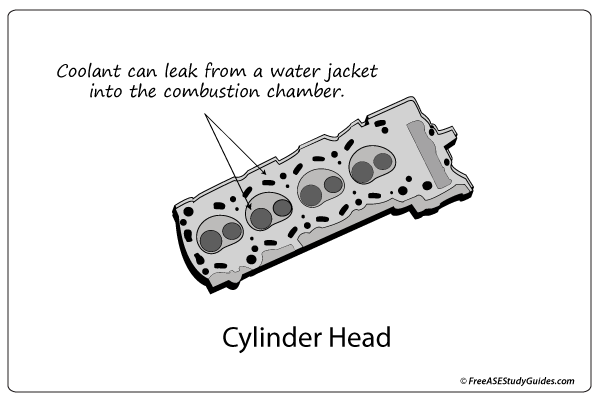
White exhaust smoke is an indication that coolant is burning in the combustion chamber. These are possible causes:
Cylinder Head: A crack in the cylinder head (around the coolant jacket) will cause coolant to enter the combustion chamber.
Engine Block: A crack in the deck of an engine block near the coolant jacket will cause coolant to enter the combustion chamber.
Head Gasket: A damaged or blown head gasket will cause coolant to enter the combustion chamber resulting in white/gray exhaust coming from the tailpipe.