Negative Temperature Coefficient Sensors

An engine coolant temperature sensor or ECT sensor is a variable resistor made of a group of metals that change resistance with temperature. Automotive manufacturers use NTC sensors, negative temperature coefficient sensors, like the engine coolant temperature sensor to indicate outside air, cabin air, and engine temperature to different control modules directly or over the CAN.
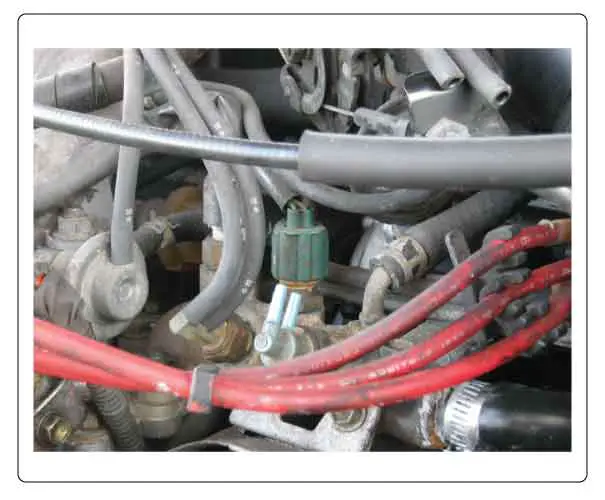

The ECT sensor's signal changes according to the engine's coolant temperature. It is a vital component for maintaining an engine's normal operating temperature. Located in the coolant stream, usually on or around the thermostat housing. The ECM uses this sensor’s input to operate the engine’s cooling fans.
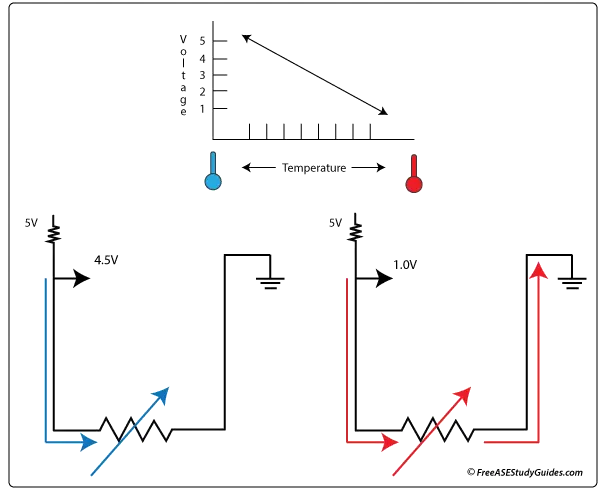
The sensor modifies a 5-volt voltage signal from the ECM concerning the engine's coolant temperature. They are (NTC) or negative temperature coefficient thermistors. This means as the coolant's temperature increases, the sensor's resistance decreases, allowing more current to pass.
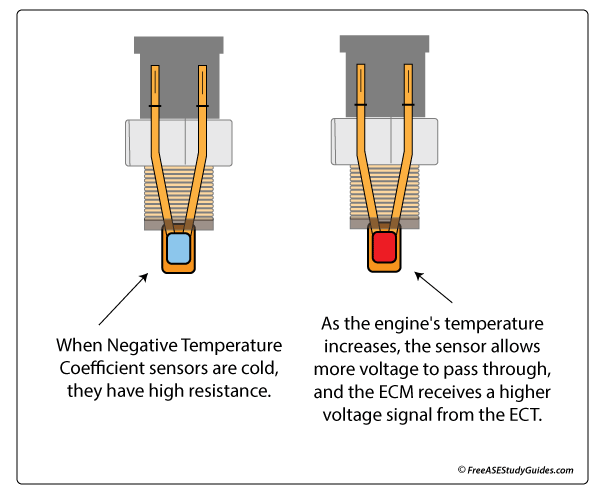
The ECM uses this signal to adjust engine cooling fans, fuel injector pulse width, and transmission (TCC) torque converter clutch actuators. While performing a voltage drop test more voltage is dropped across this sensor when the engine is cold than when it is hot. The symptoms of a faulty ECT sensor include a rich air-fuel ratio, poor fuel mileage, and an inoperative torque converter clutch.