Master Cylinder Reservoir and Cap
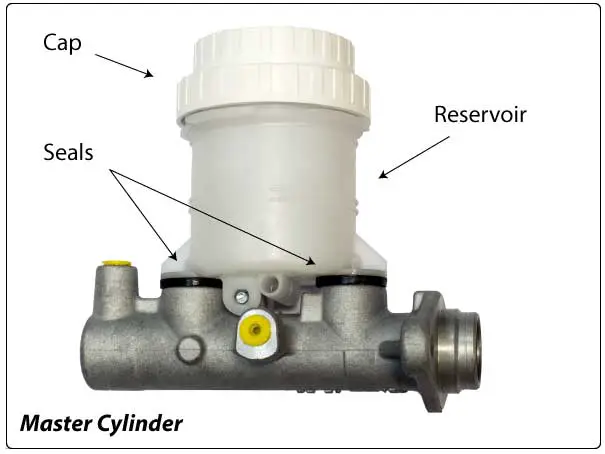
Today's vehicles have composite plastic reservoirs with a screw-on cap. A rubber gasket between the vented cap and the reservoir flexes inward to prevent air from entering the system as reservoir brake fluid levels drop.
The brake warning light will illuminate if the brake fluid level sensor indicates a low level. If it's filled to MAX, other causes may be the parking brake switch or the pressure differential switch, indicating an imbalance in brake fluid pressure.
Master Cylinder Cap Gasket
Brake fluid is hygroscopic and readily absorbs moisture from the air; the cap is vented, and the cap's gasket functions as a flexible seal, preventing contamination of the brake fluid from the environment.

Petroleum products damage the brake system's rubber components. Inspect the master cylinder's reservoir gasket for deterioration and petroleum contamination. A brake fluid flush will be necessary if the gasket's seal has swollen from contaminated brake fluid.
Brake Fluid Level
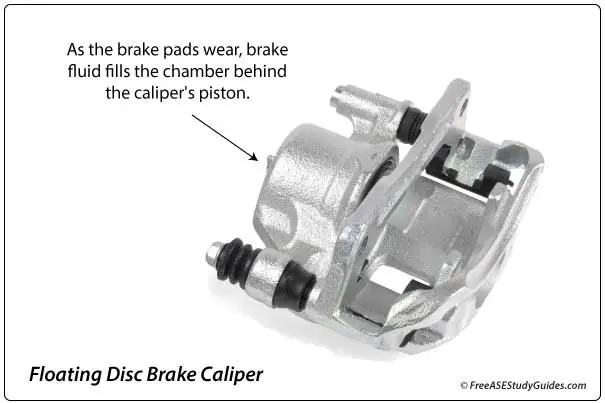

Inspect the brake system for external leaks and wear during the initial inspection. Brake fluid fills the chamber behind the caliper's piston as the pad's lining wears, lowering the level in the reservoir. As a result, the brake fluid filling the master cylinder reservoir is now taking up the extra space behind the caliper's piston. Worn brake pads will result in low master cylinder fluid levels.