Battery Testing
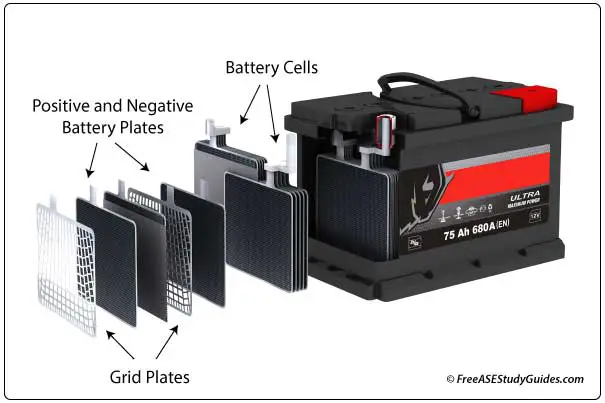
An automotive battery is a rechargeable SLI, starting, lighting, and ignition battery. It contains 12.6 volts and consists of 6 cells connected in series. A 12.6-volt automotive battery consists of six 2.1-volt cells.
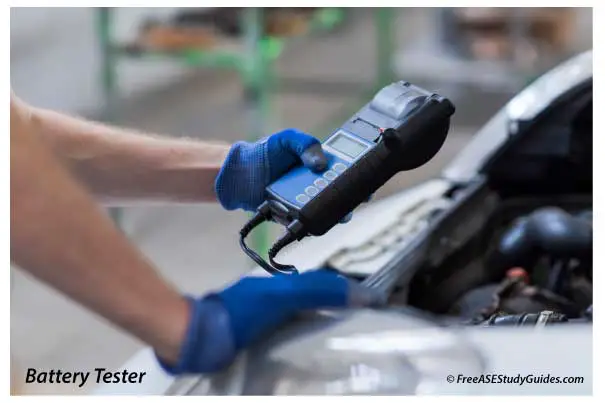

A battery's current capacity ratings measure its readiness to deliver cranking power to the starter motor and reserve energy for the electrical system.
CCA: The cold-cranking amps or cold-cranking rating determines the load or amperage the 12-volt battery can deliver for 30 seconds at 0° F without falling below 7.2 volts.
RC: The reserve capacity rating is the time it takes for the 12-volt battery to drop below 10.5 volts.
AH: The ampere-hour rating measures the steady current a battery can supply for 20 hours at 80° F without cell voltage falling below 1.75 volts.
Battery Capacity Test
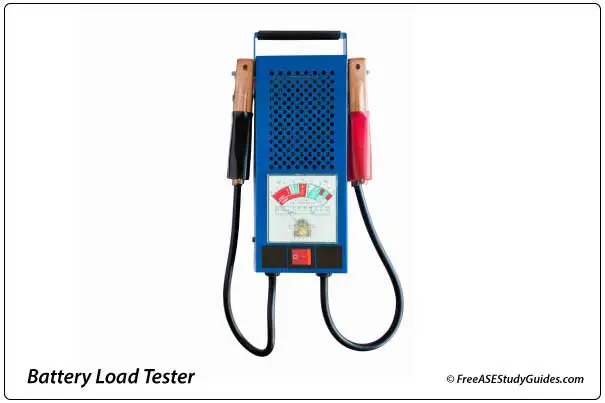


Battery Capacity Test: Perform a battery load test with a battery tester or load tester and voltage meter to see if service or replacement is necessary.
Determine the load by retrieving the CCA from the battery case and reducing this number by half. The discharge rate is one-half of the battery's cold-cranking rating. Apply this load to the battery for 15 seconds. The battery's voltage must remain above 9.6 volts at 70° F. It's relative to temperature; the lower the temperature, the lower the voltage.
Battery Specific Gravity Test
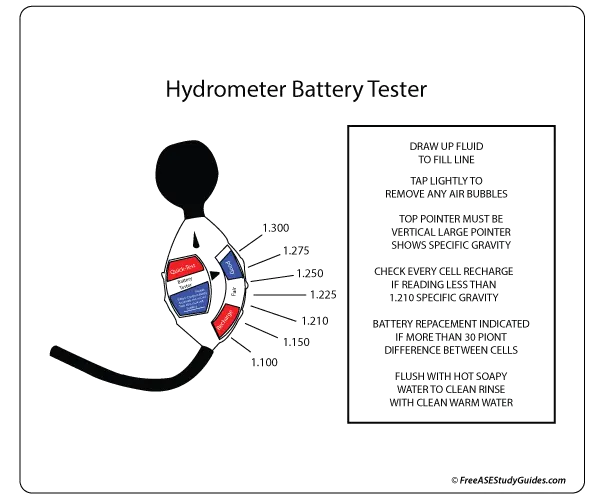
A specific gravity test determines the weight of a liquid divided by an equal amount of water. For example, a fully charged automotive battery has a specific gravity of 1.265. As the battery discharges, the specific gravity becomes lighter and more like water, closer to 1.000.
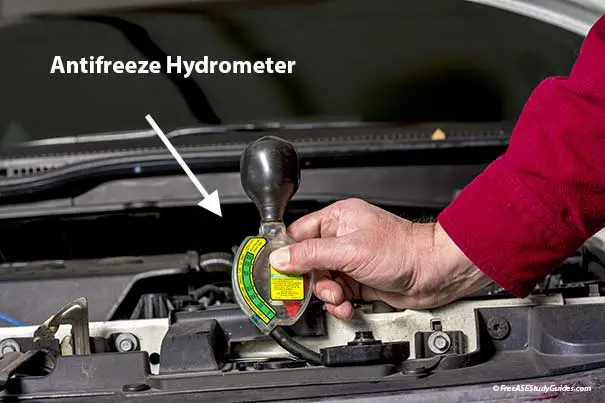

The specific gravity of a battery is a good indication of its state of charge. Use a hydrometer and adjust the reading for the outside temperature by adding or subtracting .004 for every ten degrees above or below 80° F.