Throttle Position Sensor
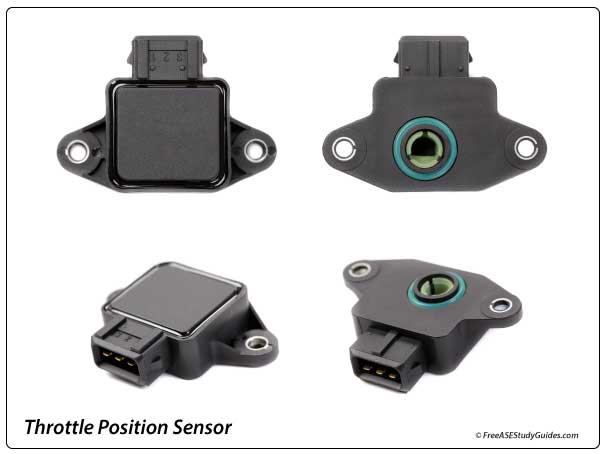

The (TPS) Throttle Position Sensor is located on the throttle body of a fuel-injected engine. It's a potentiometer, a variable resistor used to control voltage in a circuit. The TP sensor detects the engine's load by indicating the throttle plate's angle to the ECM. The compressor requires horsepower to function; to improve engine performance, the ECM opens the A/C clutch relay to disengage the clutch at WOT wide-open-throttle.
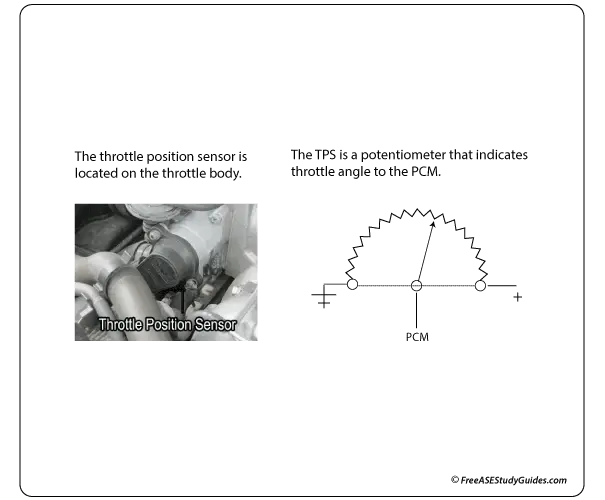
The computer's 5-volt supply voltage pin is connected to one end of the resistance strip inside of the TP sensor. The ground wire is connected to the other end of this internal resistance strip. The third wire is connected to a movable arm that swipes across this internal resistance strip, sending a varying voltage signal back to the PCM. This pin is called the signal circuit of the sensor because the lead sends the varying or "changing" voltage signal to the PCM, indicating changes in throttle angle.
The TP sensor is attached to the throttle plate shaft and changes output voltage as the throttle plate opens and closes. The output voltage is low or around 0.45 volts when the throttle is closed and is high or 4.5 volts at WOT.