A/C Condensers
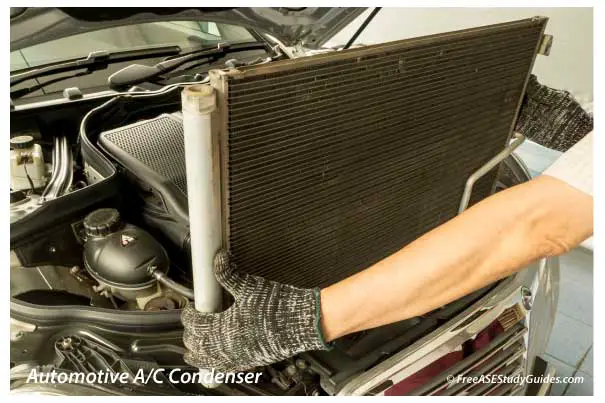

The condenser is a heat exchanger for the air conditioning system. It's located in front of the radiator and constructed of tubing surrounded by cooling fins. It releases heat into the outside air, passing through these fins. An automotive air conditioning system receives heat energy from the evaporator in the passenger's cabin. It releases the heat through the condenser to the outside air.
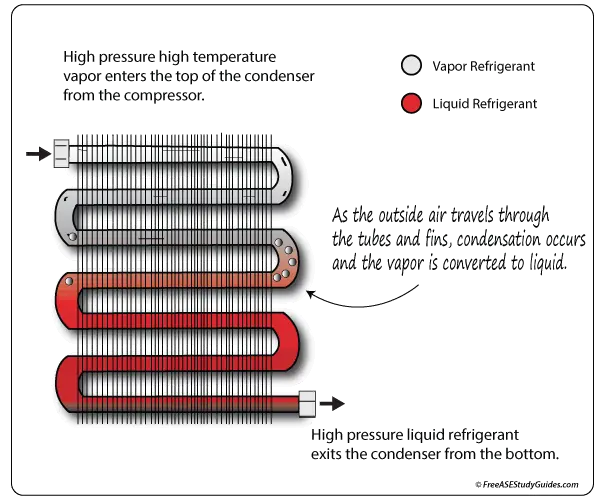
The condenser receives high-temperature, high-pressure vapor from the compressor. The heat contained in the refrigerant passes through the condenser's fins into the atmosphere. It converts the vapor into a high-pressure liquid through the process of condensation.
Vaporized refrigerant enters at the top of the condenser and travels down to the outlet at its base. The inlet at the top should be hotter to the touch than the outlet at the bottom. The liquid refrigerant flows to the receiver drier or metering device.

A non-contact infrared thermometer can be used to check for restrictions. The conversion in temperature from top to bottom should be smooth and even. Any sudden temperature changes indicate a restriction in the condenser. A restriction in an automotive air conditioning condenser results in high high side discharge pressures.