Thermostatic Expansion Valve
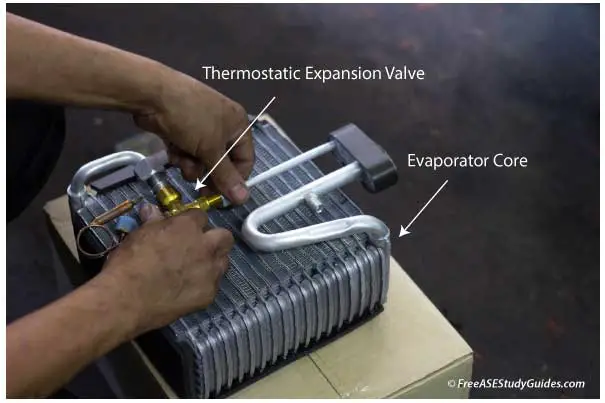
The expansion valve contains a small needle valve and diaphragm attached to a sealed gas chamber. Temperature causes the gas in this chamber to expand and contract, resulting in movement of the valve. This needle valve opens and closes to allow refrigerant into the evaporator core.
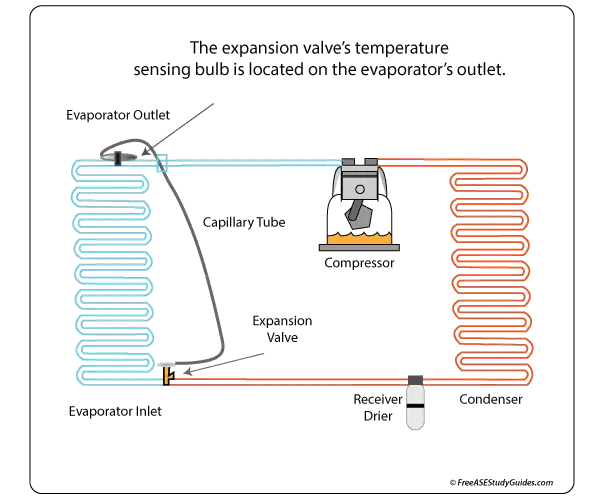
As temperatures rise, the valve opens, allowing more refrigerant into the evaporator. As it cools, the valve closes, restricting refrigerant flow into the core. This device provides optimum cooling while preventing evaporator core freeze-up.
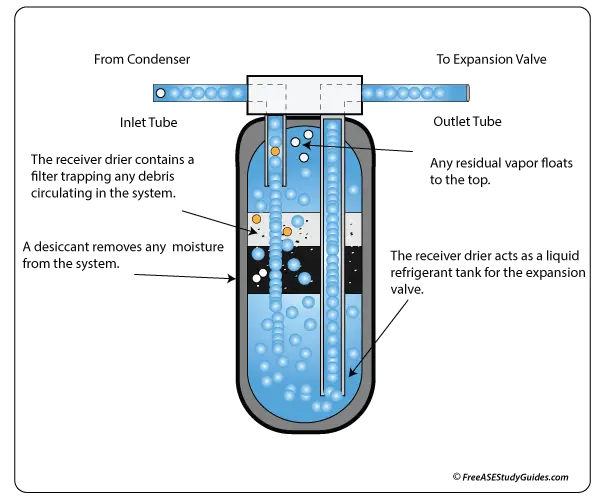
A (TXV) thermostatic expansion valve system has a receiver drier located on the high side of the system, between the condenser and the expansion valve. Accumulators and receiver driers contain a desiccant pouch to clean and absorb moisture from the refrigerant.
Fixed Orifice Tube
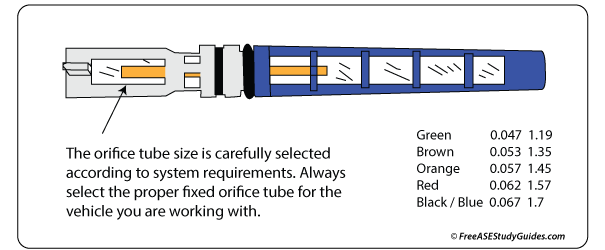
They also use a different method of metering refrigerant into the evaporator core. An (FOT) fixed orifice tube meters the same fixed amount of refrigerant based on the diameter of the tube inside its casing. A cycling clutch switch engages and disengages the compressor clutch according to the system's low side pressure.
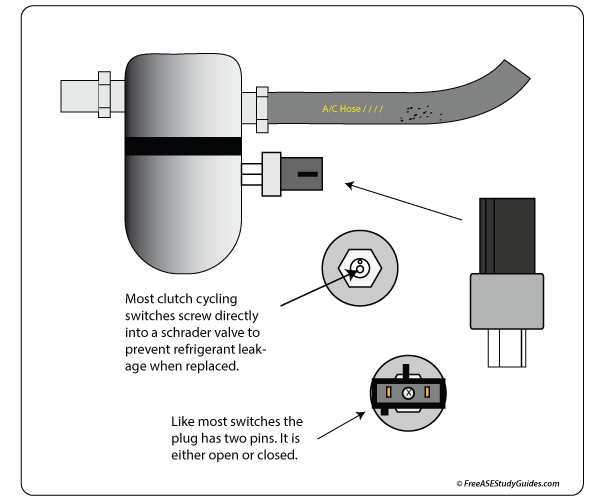
A (CCOT) cycling clutch orifice tube system has an accumulator and a cycling switch attached. The accumulator is on the low side of the system, after the orifice tube.
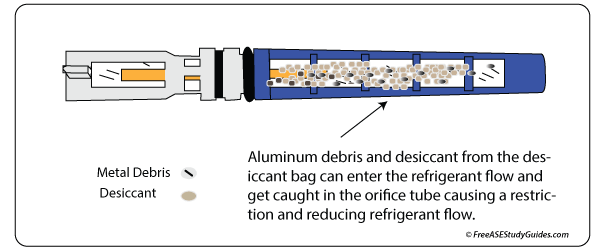
Orifice tubes can become clogged and severely hamper A/C performance. It is essential to replace the old tube with the correct tube. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations. Always check and follow the manufacturer's recommendations when replacing orifice tubes.