Starting System Components
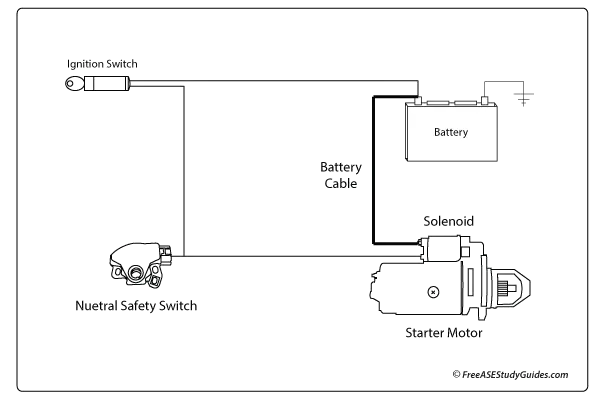
Battery Cables: Check the condition of the battery cables and perform voltage drop tests on the starter and ground cables. Battery cables come in different gauges. Years ago, battery cables were 6 gauge because only a few accessories required higher amperage.
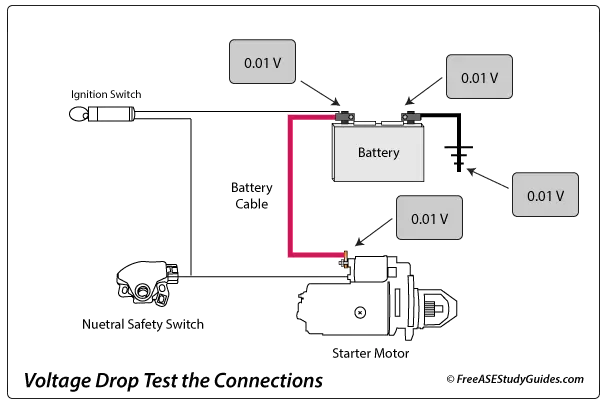
Perform voltage drop tests on the cable connections to the battery terminals, engine block, and starter terminal. Vehicles often come from the factory with 2 and 4-gauge battery cables capable of handling much higher current rates. The lower the gauge number, the thicker the cable. For instance, a 2 gauge cable is thicker than a 4 gauge cable.

Battery: Perform a voltage test using a voltage meter. A good battery will have 12.6 volts. It's 12.6 volts instead of just 12 volts because are 6 cells in series at 2.1 volts each (6 x 2.1 = 12.6). A specific gravity test is performed using a hydrometer. A fully charged battery will have a specific gravity of 1.265 at 80° F. Perform a battery load test to see if service or replacement is necessary. First, determine the load by retrieving the CCA from the battery case and reducing this number by half.
- The test discharge rate is one-half of the battery's cold-cranking rating.
- Apply this load to the battery for 15 seconds.
- The battery's voltage must remain above 9.6 volts at 70° F.
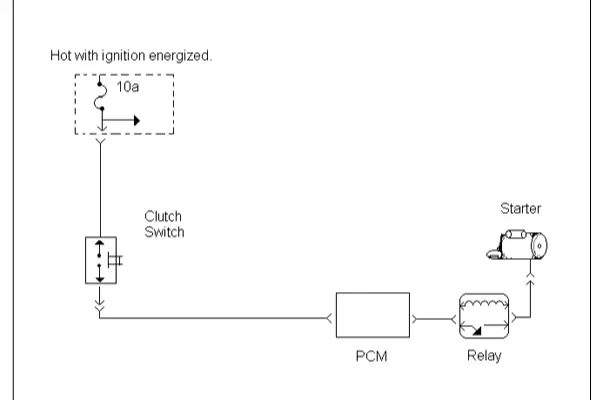
Switches: The neutral and clutch safety switches prevent startup during undesired situations. A neutral safety switch prevents starter engagement in all gears except park and neutral.
The clutch switch requires that the clutch pedal be depressed before starting the vehicle. Both of these switches are tested with an ohmmeter. Check the ignition switch to ensure it provides power to the starting circuit when placed in the start position. Starter relays are devices that use low current to control high current components.

Solenoid and Starter Motor: A starter solenoid is an electromagnetic device that serves two purposes. It completes the circuit between the battery and the starter motor. It also moves the starter's gear into mesh with the engine's ring gear.
A starter will wear, causing high current draw, and parts like the brushes, windings, and bushings must be replaced. Use an ammeter to check the starter's current draw. Compare the amperage required to turn the starter against the manufacturer's specifications.