ASE A8 Engine Performance Practice Test
36. Which of the following creates and sends an AC voltage signal to the ECM when it detects detonation?
- A. The throttle position sensor.
- B. The knock sensor.
- C. The manifold absolute pressure sensor.
- D. The oxygen sensor.
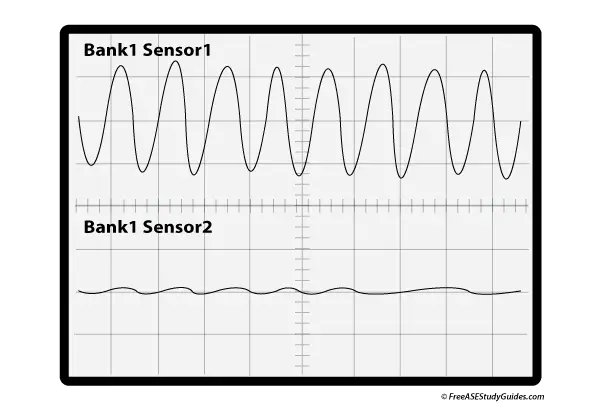
37. Bank 1 Sensor 1 is the pre-catalytic converter heated oxygen sensor, and Bank 1 Sensor 2 is the post-catalytic converter heated oxygen sensor. Technician A says to replace the Bank 1 Sensor 2 because the two waveforms should have similar voltage peaks and fluctuations. Technician B says Bank 1 Sensor 2 monitors the catalytic converter's ability to reduce pollutants in the exhaust stream. Who is correct?
- A. Technician A
- B. Technician B
- C. Both A and B
- D. Neither A or B
38. An engine with variable valve timing has a rough idle but runs smoothly at higher speeds. Technician A says to check the variable valve timing solenoid and its associated circuit. Technician B says this problem can be caused by unchanged contaminated oil. Who is correct?
- A. Technician A
- B. Technician B
- C. Both A and B
- D. Neither A or B
39. Technician A says an (AF) air-fuel ratio sensor senses a broader range of air-fuel mixtures than a standard oxygen sensor. Technician B says stoichiometry is 15.7:1 air to fuel mixture. Who is correct?
- A. Technician A
- B. Technician B
- C. Both A and B
- D. Neither A or B
40. A vehicle has poor acceleration. A vacuum gauge is connected to the engine's intake manifold. While steadily increasing the engine speed to 2500 RPM, the needle on the gauge drops slowly to 10 "hg. Which of these could be the cause?
- A. A clogged catalytic converter.
- B. Late valve timing.
- C. A faulty head gasket.
- D. Burned exhaust valve.